Casual Labour Tax Rules Canada
Those days are long gone.

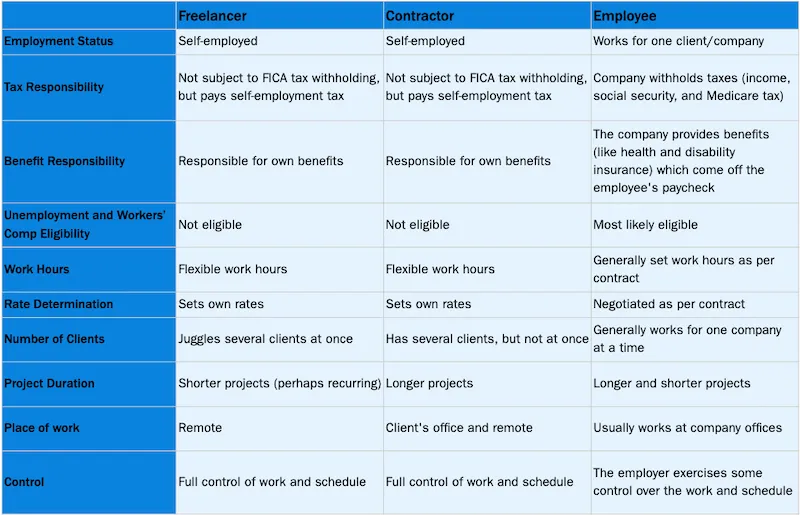
Casual labour tax rules canada. Casual employment if it is for a purpose other than your usual trade or business. The remuneration received for services is 50 or more and the services which are not in the course of. There are only two employment options available for tax filings subcontractor or employee. Employment as a teacher on exchange from a foreign country.
Until about 10 years ago the canada revenue agency cra accepted casual labour as a valid expense. Now when you hire someone they are either an employee or a subcontractor. In either case an employer must have an individuals social insurance number on file. Election to pay cpp contributions in cases where the employment is not pensionable if conditions are met the employee can elect to pay cpp contributions on the earnings by completing form cpt20 election to pay canada pension plan contributions.
Employment of a spouse or common law partner if you cannot deduct the remuneration paid as an expense under the income tax act. Students in the holidays the chances are they wont have a p45 form a previous job. Therefore the employment meets the two conditions for casual employment and the employment is not pensionable or insurable. Casual workers are hired for specified periods that may not exceed 90 working days in one calendar year in a department or in an agency to which the public service commission psc has exclusive authority to make appointments.
When casual labour starts to look complicated. Casual labor be excluded from employment. Since the rules for casual labour changed in canada the only two employment options available for tax filings are subcontractor or employee and in either case an employer must have the individuals social insurance number on file. Once upon a time the canada revenue agency cra would allow you to deduct small payments made to people that you hired to do a particular job or maybe work a few hours to cover someone a student to hand out fliers etc and it was called casual labour.
The period of casual employment may be for one or more than one term but is not to exceed 90 working days in a department or agency in a calendar year. In this case you should give them the usual starter checklist to complete to establish the correct code to operate.



/_what-you-should-know-before-visiting-canada-1481860-v4-5bd9abff46e0fb002d2e87e8.png)








/when-you-can-expect-to-get-your-first-and-last-paycheck-2060057_FINAL-5c6c1bc446e0fb000165cba9.png)












/https://www.thestar.com/content/dam/thestar/news/canada/2020/03/25/live-friday-at-noon-et-toronto-employment-lawyer-answers-your-questions-about-worker-rights-during-covid-19/soma_rayellis_ts.jpg)















/arc-anglerfish-tgam-prod-tgam.s3.amazonaws.com/public/6MVY2MXM6ZFHVNXCD6EWBCRF5I)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():saturation(0.2):brightness(10):contrast(5)/woman-and-young-girl-embracing-outdoors-77931650-5a8061e7875db9003796093d.jpg)



/potter-entrepreneur-using-laptop--in-workshop-639534022-5b2ea61b3de42300363ca809.jpg)






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():saturation(0.2):brightness(10):contrast(5)/work-injury-173894582-57ab99b05f9b58974a634daf.jpg)







/492717447-56a03f505f9b58eba4af84f5.jpg)









/https://www.thestar.com/content/dam/thestar/news/canada/2020/03/27/worker-rights-live-chat-toronto-employment-lawyer-hermie-abraham-answers-your-questions-monday-at-noon-et/hermiea.jpg)
/GettyImages-124203414-94019aed4fdd441ea476e1c9deebdd15.jpg)


/work-injury-173894582-57ab99b05f9b58974a634daf.jpg)